Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) are two prominent therapeutic approaches that have transformed the landscape of mental health treatment. While both are rooted in psychology, their focus and methodologies diverge.
CBT identifies and alters negative thought patterns and behaviors, promoting adaptive coping strategies. In contrast, DBT combines traditional CBT techniques with mindfulness and acceptance strategies to address emotional dysregulation and complex issues, particularly in borderline personality disorder and self-harm cases.
Understanding the applications and comparative effectiveness of CBT and DBT is essential in enhancing individuals’ well-being and psychological resilience.
Key Takeaways
Remember, therapists may integrate elements from both therapies based on the client’s needs. Here’s what you need to know about CBT VS. DBT:
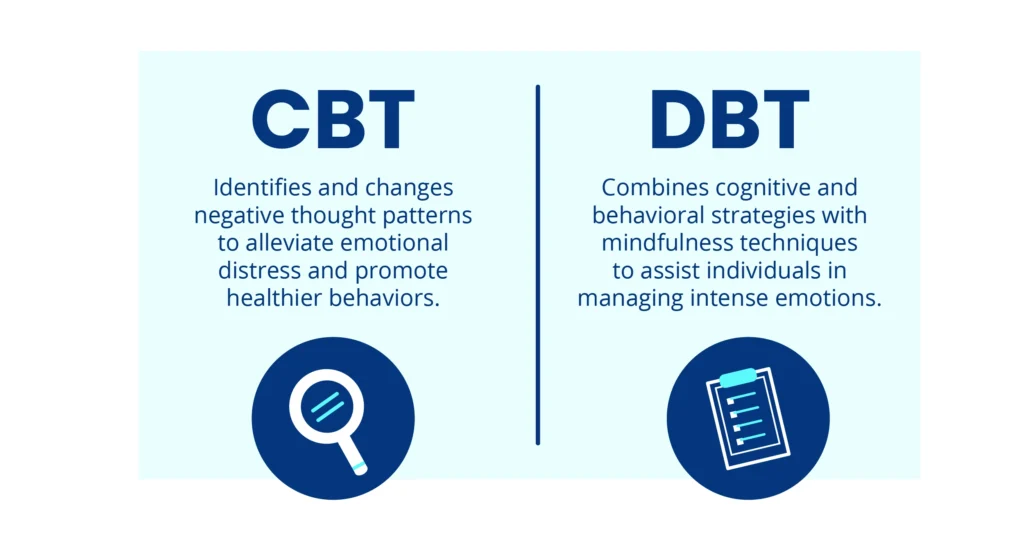
- CBT identifies and changes negative thought patterns to alleviate emotional distress and promote healthier behaviors.
- DBT combines cognitive and behavioral strategies with mindfulness techniques to assist individuals in managing intense emotions and building interpersonal skills.
- The choice between CBT and DBT depends on the individual’s needs and the nature of their presenting concerns.
Contact The Haven Detox-New England at (844) 933-4145 for personalized assistance to foster long-term recovery and growth.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), a talk therapy, is one of the most widely practiced and evidence-based forms of psychotherapy. Rooted in the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected, CBT believes that changing negative thought patterns can lead to positive behavioral changes and improved emotional well-being.
Key Principles of CBT
Identifying Cognitive Distortions: CBT helps individuals recognize cognitive distortions and biased or irrational ways of thinking contribute to negative emotions. These distortions can include all-or-nothing thinking, overgeneralization, catastrophizing, and personalization.
Thought Restructuring: It helps individuals restructure their thoughts by examining evidence for and against their negative beliefs once cognitive distortions are identified. This process encourages more balanced and realistic thinking patterns.
Behavioral Activation: CBT often includes strategies to increase engagement in positive and rewarding activities, which can help alleviate symptoms of depression and other mood disorders.
Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is a common technique used in CBT for individuals dealing with anxiety and phobias. It involves gradually exposing the individual to the feared situation or object in a controlled and supportive environment, helping them build tolerance and reduce anxiety.
Skill Building: CBT provides individuals with coping skills and techniques to manage stress, regulate emotions, and solve problems effectively. These skills are intended to empower individuals to handle challenging situations more healthily.
Homework and Practice: CBT often involves assigning homework tasks that encourage clients to practice the skills and techniques learned during therapy sessions in real-life situations.
How Is CBT Practiced
CBT typically follows a structured format. Initially, the therapist and client work together to identify the problematic thought patterns contributing to the client’s distress. This could involve recognizing negative self-talk, unrealistic expectations, or catastrophic thinking.
Once identified, the therapist helps the client challenge these thoughts by providing evidence to the contrary. Gradually, this process can lead to a more balanced and realistic perspective. Simultaneously, CBT encourages behavioral experiments testing new behaviors or ways of thinking to reinforce positive change.
Homework assignments often play a significant role in CBT, encouraging the client to practice new skills outside therapy sessions.
Benefits and Limitations
CBT offers a range of benefits. Its practical nature and focus on skill-building make it applicable to various mental health issues, including anxiety disorders, depression, phobias, and stress. The collaborative relationship between therapist and client empowers individuals to participate in their recovery actively.
Moreover, the skills acquired in CBT can be lifelong tools for managing future challenges. However, CBT has its limitations. Its structured approach might only resonate with some; some prefer more exploratory or insight-oriented therapies.
Additionally, its focus on the present may not address deep-rooted traumas or issues that originated in the past. CBT’s effectiveness also relies on the client’s willingness and ability to engage in self-monitoring and homework assignments.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
DBT therapy is a comprehensive and evidence-based therapeutic approach that has gained significant recognition for its effectiveness in treating various mental health disorders, especially those characterized by emotional dysregulation and self-destructive behaviors.
Developed by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan in the late 1980s, DBT integrates cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness practices, offering individuals a structured path to build healthier coping mechanisms and emotional resilience.
Key Principles of DBT
Dialectics: At the core of DBT is the principle of dialectics, which acknowledges the tension between change and acceptance. It teaches clients to balance the need for change with radical acceptance of their current emotional states and circumstances. This helps individuals avoid extreme thinking and find a middle ground, fostering personal growth.
Mindfulness: Research claims DBT emphasizes the cultivation of mindfulness skills. Mindfulness involves paying non-judgmental attention to the present moment, promoting self-awareness and reducing reactivity. This practice enables individuals to observe their thoughts, emotions, and chronic pain without being overwhelmed, leading to better emotional regulation.
Distress Tolerance: Learning to tolerate distressing situations without resorting to destructive behaviors is another key aspect of DBT. Clients acquire skills to manage intense emotions without impulsively reacting, avoiding impulsive actions that might exacerbate their distress.
How Is DBT Practiced
DBT comprises four key modules: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. These modules are taught in both individual and group therapy settings. Mindfulness helps individuals become aware of their thoughts, feelings, and sensations in the present moment without judgment.
Distress tolerance equips patients with skills to manage crises and tolerate distressing situations without resorting to harmful behaviors. Emotion regulation assists individuals in identifying and managing intense emotions that often lead to impulsive actions.
Interpersonal effectiveness focuses on improving communication and relationship skills.
Benefits and Limitations
DBT offers several benefits, including enhanced emotional regulation, reduced impulsive behavior, improved interpersonal relationships, and increased overall well-being. It has been found effective for borderline personality disorder and other conditions like depression, anxiety, substance use disorders, and eating disorders.
The emphasis on mindfulness contributes to stress reduction and increased self-awareness. However, DBT also has its limitations. The treatment demands significant commitment from both the therapist and the individual, requiring a long-term investment in therapy.
Some individuals struggle with mindfulness, finding it challenging to practice and integrate it into their daily lives.
Comparing DBT and CBT
DBT and CBT are both types of psychotherapy widely used to help people manage and cope with various mental health challenges. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct approaches and focuses.
Here’s a comparison of DBT and CBT:
Origin and Founders
- DBT: Developed by Marsha M. Linehan, DBT was initially designed to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder and chronic suicidal thoughts.
- CBT: CBT has roots in the work of various psychologists, but Aaron T. Beck is often credited as one of its founders. It has evolved into different forms, including traditional CBT and newer variations like Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT).
Focus
- DBT: Primarily focuses on emotional regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness. It aims to help individuals manage intense emotions, improve relationships, and develop coping skills.
- CBT: Focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to psychological distress. It aims to modify irrational beliefs and cognitive distortions.
Mindfulness
- DBT: Emphasizes mindfulness as a core component. Mindfulness techniques are taught to help individuals stay present in the moment and observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment.
- CBT: While mindfulness can be incorporated, it’s not a central component of traditional CBT. However, newer variations like Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) integrate mindfulness practices more explicitly.
Targeted Conditions
- DBT: Initially developed for borderline personality disorder, DBT has been adapted to treat various conditions, including mood disorders, eating disorders, substance use disorders, and more.
- CBT: Widely used to treat various mental health issues, including depression, anxiety disorders, phobias, panic disorder, OCD, PTSD, and more.
Techniques
- DBT: Besides individual therapy, DBT often includes group therapy sessions where interpersonal skills and distress tolerance techniques are practiced. It uses strategies like validation, problem-solving, and acceptance.
- CBT: Focuses on identifying and challenging cognitive distortions through structured sessions. It often involves homework assignments to practice new thought patterns and behaviors outside therapy.
Change Vs. Acceptance
- DBT: Incorporates elements of both change and acceptance. It recognizes that change is necessary but also emphasizes acceptance of oneself and one’s emotions.
- CBT: Primarily emphasizes changing negative thought patterns and behaviors through rational examination and modification.
Timeframe
- DBT Often involves a longer duration of treatment due to its comprehensive approach and focus on multiple skill areas.
- CBT: This can vary in duration, but it often involves a more structured and shorter-term treatment plan.
Suitability
- DBT: Well-suited for individuals with intense emotional dysregulation, self-harm tendencies, and difficulty managing relationships.
- CBT: Suitable for many individuals experiencing different cognitive and behavioral challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is DBT or CBT more effective?
DBT (Dialectical Behavior Therapy) and CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy) are effective psychotherapeutic approaches, but their effectiveness depends on the individual’s needs and conditions.
DBT is often used for managing intense emotions and borderline personality disorder, while CBT addresses various mental health issues. The choice between them should be based on the individual’s diagnosis and treatment goals.
What is the main difference between DBT and CBT?
The main difference between DBT and CBT lies in their focus and application. DBT emphasizes managing emotions, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness, making it suitable for individuals with intense emotions or borderline personality disorder.
Conversely, CBT identifies and changes negative thoughts and behaviors, making it versatile for various mental health conditions, including substance abuse, suicidal ideation, and anxiety.
Why is DBT criticized?
DBT (Dialectical Behavior Therapy) has faced criticism for its intensive time commitment, as it often involves both individual therapy and group sessions. Some critics argue that the skills taught in DBT can be complex to implement effectively.
Additionally, its structure and adherence to a manualized approach have been criticized for potentially limiting therapist creativity and tailoring to individual needs.
Find Lasting Relief at The Haven Detox-New England
Discover solace and healing at The Haven Detox-New England. Embrace a path to serenity through our comprehensive mental health services tailored to combat stress, anxiety, and the negative emotional triggers that may fuel addiction and other problems.
Our distinguished services can be your fortress of recovery, nurturing lasting healing. One of our effective programs is residential treatment, where therapy is integral to after-care.
Our medical professionals, including therapists, will guide you towards the therapy tailored to your specific needs. We focus on cultivating effective coping mechanisms and fostering a life of vitality and wellness.
Release yourself from the chains of co-occurring disorders. Find relief, renewal, and transformation. Contact us at (844) 933-4145 to schedule your appointment.