MAT medication, or medication-assisted treatment, is a highly effective approach to combating addiction. It involves using FDA-approved medications in combination with counseling and behavioral therapies.
MAT medication aims to minimize withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings, and normalize brain chemistry, enabling individuals to regain control of their lives. This evidence-based treatment approach not only helps manage addiction to opioids and alcohol but also supports recovery from other substance use disorders.
Key Takeaways
MAT has improved treatment outcomes and reduced overdose deaths. Here’s what you need to know about this life-saving addiction treatment:
- MAT (medication-assisted treatment) combines medication with therapy to treat substance use disorders effectively.
- MAT reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms, increasing the chances of successful recovery.
- Medications commonly used in MAT include methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone.
- MAT should be tailored to individual needs, with ongoing monitoring and adjustments to medication dosages as necessary.
Contact The Haven Detox-New England (844) 933-4145 for reliable medical advice for long-term healing.
Opioid Overdose Epidemic
The opioid overdose epidemic continues to devastate communities across the globe. This public health crisis has claimed countless lives and shattered families. Opioids, prescription painkillers, and illicit drugs like heroin have become alarmingly pervasive, leading to a surge in overdose deaths.
Factors contributing to this epidemic include overprescription of opioid medications, addiction, and the availability of potent synthetic opioids like fentanyl. Urgent action is required to address this crisis. This includes improving access to addiction treatment, implementing stricter prescription guidelines, increasing public awareness about the risks of opioid misuse, and enhancing law enforcement efforts to combat illicit drug trafficking.
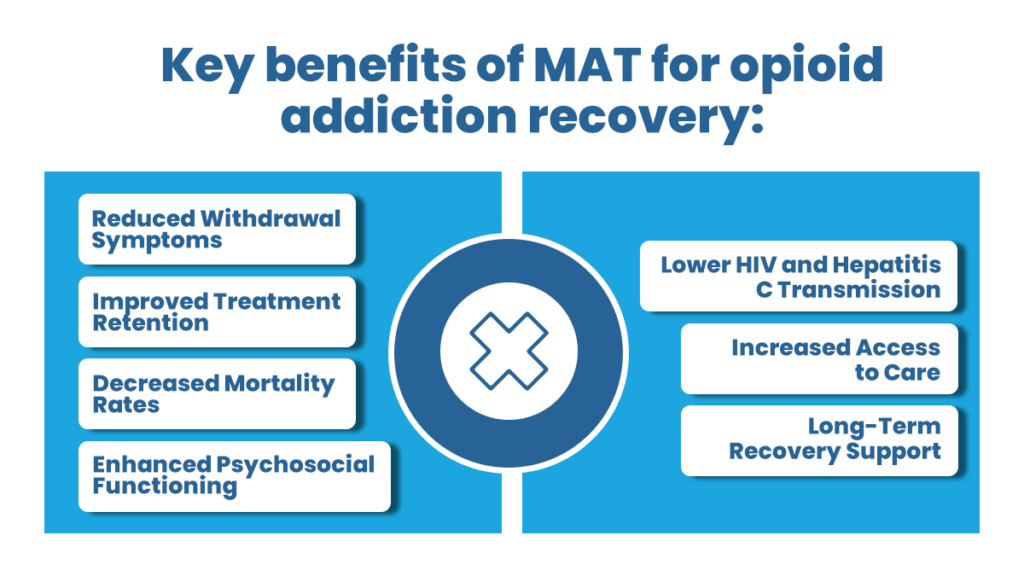
Benefits of MAT for Opioid Addiction Recovery
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) has emerged as a highly effective approach for supporting individuals recovering from opioid addiction.
Here are some key benefits of MAT for opioid addiction recovery.
- Reduced Withdrawal Symptoms: MAT helps alleviate the severe withdrawal symptoms of opioid addiction. Medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone can stabilize brain chemistry, reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. This allows individuals to focus on recovery without withdrawal’s debilitating physical and psychological effects.
- Improved Treatment Retention: MAT has been shown to improve treatment retention rates. By managing cravings and withdrawal symptoms, medications enable individuals to stay engaged in treatment for longer. Extended treatment duration increases the likelihood of successful recovery outcomes, reducing the risk of relapse.
- Decreased Mortality Rates: Opioid addiction is associated with a high risk of overdose and mortality. MAT reduces the risk of fatal overdoses significantly. Medications like naloxone, commonly used in MAT, can reverse the effects of opioid overdose, providing a life-saving intervention in emergencies.
- Enhanced Psychosocial Functioning: MAT allows individuals to regain control over their lives by stabilizing brain chemistry and reducing cravings. With a clearer mind, they can actively participate in counseling and behavioral therapies, addressing the underlying issues contributing to addiction. MAT facilitates better decision-making, emotional stability, and improved overall psychosocial functioning.
- Lower HIV and Hepatitis C Transmission: Substance abuse often goes hand in hand with risky behaviors such as sharing needles, leading to a higher risk of infectious diseases like HIV and hepatitis C. MAT programs include harm reduction strategies, such as providing clean needles and education on safe injection practices. MAT lowers the transmission rates of these diseases by reducing drug use and associated risky behaviors.
- Increased Access to Care: MAT programs offer increased accessibility to addiction treatment. Primary care providers can prescribe certain medications for opioid addiction, reducing the barriers to entry into treatment. Expanding access to MAT allows more individuals to seek help, particularly in underserved areas where specialized addiction treatment services may be limited.
- Long-Term Recovery Support: MAT is effective during the acute phase of addiction treatment and provides long-term support for sustained recovery. Medications can be prescribed for extended periods, supporting individuals in maintaining abstinence and preventing relapse. The combination of medication and psychosocial support significantly enhances the chances of long-term recovery success.
Medications Used in MAT
Medications used in MAT have revolutionized the approach to addiction recovery. Three primary medications are commonly used in MAT, including:
Methadone
Methadone is a synthetic opioid agonist that reduces withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Administered under strict medical supervision, it helps individuals stabilize their lives while minimizing illicit drug use.
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist, also alleviates withdrawal symptoms and cravings but has a lower risk of overdose than full opioid agonists. It can be prescribed in office-based settings, making it more accessible for patients.
Naltrexone
Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, blocks the effects of opioids and prevents relapse. It is available in both oral and extended-release injectable formulations. Each medication has unique benefits and considerations, and the choice depends on individual circumstances, such as the severity of addiction and patient preference.
MAT for Other Addictions
MAT is commonly used for OUD but can also be used for other substance addictions. While opioids are the most well-known substance for which MAT is used, medications can also be prescribed to treat other addictions.
Here are a few examples:
- Alcohol Addiction: Medications such as naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram can help people with alcohol use disorder. Naltrexone works by reducing the cravings and pleasurable effects of alcohol, while acamprosate helps to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Disulfiram creates unpleasant reactions when alcohol is consumed, acting as a deterrent.
- Tobacco Addiction: Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is a common form of MAT used for tobacco addiction. This includes nicotine patches, gums, lozenges, inhalers, and nasal sprays, which provide controlled doses of nicotine to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- Stimulant Addiction: There is no FDA-approved medication specifically for stimulant addiction, such as cocaine or methamphetamine. However, some medications used for other conditions, such as bupropion and modafinil (used for narcolepsy and shift work sleep disorder), have shown some promise in reducing cravings and supporting abstinence in individuals with stimulant addiction.
- Cannabis Addiction: There is limited research on medications for cannabis addiction. However, some medications, such as dronabinol (synthetic THC) and nabilone (synthetic cannabinoid), have been explored for their potential to reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
How to Choose A MAT Facility
When choosing a MAT facility, several factors must be considered to ensure you receive the appropriate care and support for your needs.
Here are some steps to help you make an informed decision:
- Research MAT Facilities: Research different MAT treatment centers in your area. Look for facilities that specialize in addiction treatment and offer MAT services. You can find information about these facilities online, through referrals from healthcare professionals, or by contacting local substance abuse hotlines.
- Accreditation and Licensing: Check if the facility is accredited and licensed by the appropriate regulatory bodies. Accreditation ensures that the facility meets specific quality standards and adheres to best practices in addiction treatment.
- Treatment Approach: Learn about the treatment approach used by the MAT facility. MAT typically combines medication, such as methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone, with counseling and behavioral therapies. Ensure that the facility offers a comprehensive approach that addresses addiction’s physical and psychological aspects.
- Qualified Staff: Assess the qualifications and expertise of the facility’s staff. MAT requires a multidisciplinary team, including doctors, nurses, counselors, and therapists. Check if the staff members are licensed and experienced in addiction medicine and counseling.
- Accessibility and Location: Evaluate the facility’s accessibility and location. Ideally, choose a facility that is conveniently located and easily accessible to ensure regular attendance for medication management and therapy sessions.
- Insurance Coverage: Check if the MAT facility accepts your health insurance or if they offer affordable payment options. Understanding the financial aspect will help you plan for the cost of treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is MAT the same as Suboxone?
No, MAT and Suboxone are not the same. MAT, or medication-assisted treatment, is a comprehensive approach to treating substance use disorders that combines medications, such as Suboxone, with counseling and behavioral therapies.
Suboxone, on the other hand, is a specific medication used in MAT programs to help manage opioid dependence.
What is the main goal of MAT treatment?
The main goal of MAT treatment is to provide therapy and support for individuals struggling with substance abuse or addiction. It involves the administration of medication, such as methadone or buprenorphine, to alleviate withdrawal symptoms and cravings while also addressing underlying psychological and behavioral issues.
Mat treatment aims to stabilize patients, reduce drug use, and improve overall quality of life.
What are examples of MAT medications?
Examples of MAT (medication-assisted treatment) medications include methadone, buprenorphine (Suboxone), naltrexone (Vivitrol), and naloxone (Narcan). These medications are commonly used to treat opioid use disorder and help reduce cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and the risk of overdose.
Transform Your Life at The Haven Detox-New England
Whether you’re battling opioid dependency, alcohol abuse, or heroin addiction, The Haven Detox-New England is here to provide a helping hand.
With our unwavering commitment to your well-being, we offer a comprehensive range of services, including detoxification, residential programs, and evidence-based therapies. Our highly trained and compassionate experts will guide you every step of the way, ensuring you receive personalized care tailored to your unique needs.
Furthermore, our dual diagnosis program addresses the connection between substance abuse and co-occurring mental health disorders, fostering lasting healing and recovery.
Embrace the opportunity to transform your life today. Reach out to The Haven Detox-New England (844) 933-4145 to start your journey towards a healthier and happier tomorrow.



