Heroin use can have profound and alarming effects on individuals, impacting their physical and mental well-being. Identifying the signs of heroin use is vital for early intervention and support.
This information equips individuals with the knowledge to identify potential heroin use. This way, we foster a proactive approach to seeking professional assistance and promoting overall community well-being.
Key Takeaways
Heroin, a powerful opioid derived from morphine, is a highly addictive and illegal drug.
- The use of heroin can lead to a decline in overall functioning, with individuals failing essential responsibilities.
- Heroin disrupts sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and a persistent feeling of fatigue.
- If you or someone you know is facing the challenges of heroin use, reach out for assistance toward a healthier future.
The Haven Detox-New England provides compassionate and personalized services to those on their journey to recovery. Call us at (844) 933-4145 to explore our services that revive your life.
What Is Heroin?
Heroin, a powerful opioid derived from morphine, is a highly addictive and illegal drug. It belongs to the opiate class of substances, initially synthesized from the opium poppy plant.
Identifying the signs of heroin use is vital for both individuals and communities to address potential health risks promptly. Being informed about the physical, behavioral, and psychological indicators empowers individuals to identify early warning signs and seek professional help.
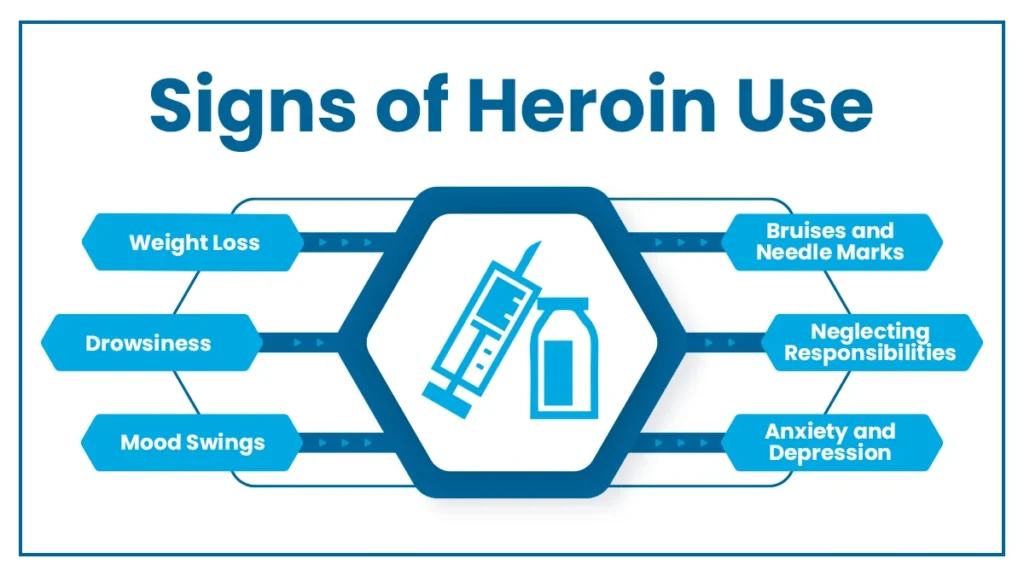
Signs of Heroin Use
Heroin poses significant risks to individuals and communities alike. The subtle yet impactful cues that may signal the presence of heroin use:
- Weight Loss: Heroin use often leads to a significant and sudden reduction in body weight, and Individuals may appear gaunt and malnourished due to the drug’s impact on appetite and metabolism.
- Drowsiness: Excessive lethargy and drowsiness are common physical signs of heroin use, and people may struggle to stay awake, nodding off at inappropriate times.
- Bruises and Needle Marks: The injection of heroin can result in visible bruising and needle marks commonly found on the arms, hands, or other areas where injections occur.
- Neglecting Responsibilities: The use of heroin can lead to a decline in overall functioning, with individuals failing essential responsibilities at work, home, or school.
- Changes in Behaviors: People often exhibit erratic behaviors, such as increased secrecy, isolation, or unexplained mood swings. Social withdrawal and changes in friend circles are also observed.
- Mood Swings: Heroin significantly affects mood regulation, causing abrupt and unpredictable mood swings. Individuals may shift from euphoria to irritability or aggression.
- Anxiety and Depression: Heroin use is linked to the development of anxiety and depression. The drug’s impact on neurotransmitters contributes to mental health disturbances.
Being vigilant about the signs of heroin use is essential for promoting individual well-being and community health. Always offer support to those who may be grappling with the challenges of heroin dependency.
Short-Term Effects of Heroin Use
Heroin use induces immediate and intense effects on the body, resulting in several short-term consequences:
Nausea and Vomiting: Heroin use commonly leads to nausea and vomiting, contributing to a cycle of discomfort for the user. These symptoms may occur shortly after drug administration.
Itching: Heroin use can cause intense itching, often called itchy blood. This itching sensation results from the drug’s impact on histamine release in the body.
Slowed Heart Rate: One of the critical effects of heroin is the slowing of the heart rate. It can lead to dangerous cardiovascular complications, emphasizing the acute risks associated with heroin use.
Long-Term Effects of Heroin Use
Chronic heroin use has lasting consequences on both physical and mental health. Long-term effects include:
Insomnia: Heroin disrupts sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and a persistent feeling of fatigue. Sleep disturbances contribute to the overall decline in health and well-being.
Kidney or Liver Disease: The toxins present in heroin can damage vital organs over time, with prolonged use increasing the risk of kidney or liver disease. Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor organ function.
Collapsed Veins: Frequent injection of heroin can cause veins to collapse or become damaged. It not only poses immediate risks during drug administration but also complicates medical procedures such as blood tests or intravenous interventions.
Heroin Use and Personal Life
Heroin use not only affects physical health but also takes a toll on personal life. The profound impact on relationships, responsibilities, and overall well-being is discussed in the following discussion.
Affected Relationships: Heroin use strains relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners. The behavioral and emotional changes associated with drug dependency can create rifts and hinder effective communication.
Disruption to Work or School: The neglect of responsibilities, decreased productivity, and unpredictable behaviors resulting from heroin use can disrupt educational pursuits or professional endeavors. Job loss and academic setbacks are expected consequences.
When to Seek Help
Identifying the signs of heroin use, such as withdrawal symptoms and overdose risk, is essential for seeking help. If a person exhibits symptoms like increased tolerance, a black sticky substance named black tar heroin, or experiences withdrawal, it’s time to consider professional assistance. Family members can play a pivotal role by supporting their loved ones through recovery.
Environmental factors, genetics, and personal influences contribute to heroin use disorder. The central nervous system depressant nature of heroin poses an increased risk of overdose, especially when mixed with other substances like alcohol or medication. Knowing the risk factors and the ability of heroin to affect opioid receptors in the brain is vital to reducing the risks.
If someone is grappling with heroin addiction, seeking treatment is imperative. Therapies, both behavioral and medicinal, are available. Medical attention is essential during withdrawal to manage symptoms and reduce the rush for continued use.
Experts stress the importance of addressing heroin abuse promptly, considering the environmental influences, personality traits, and the role of genetics. Awareness of these factors can aid in developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. If you or someone you know is facing the challenges of heroin use, reaching out for assistance is a crucial step towards a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can behavioral changes signify heroin abuse, and what are they?
Behavioral changes can indicate heroin abuse. Common signs include erratic mood swings, neglect of personal responsibilities, and withdrawal from social activities.
Heroin, an illicit drug, swiftly crosses the blood-brain barrier, causing immediate effects on brain chemistry. Researchers link drug addiction to genetic components; those with a first-degree relative facing substance abuse are at higher risk.
Heroin abuse manifests in track marks, low blood pressure, and a brown powder’s presence. Teens with a family history of substance abuse are particularly vulnerable. If someone exhibits these symptoms, seeking medical care and long-term recovery services is crucial. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control highlights the alarming rise in opioid use disorders, highlighting the need for awareness and prevention.
What are the signs that someone has a heroin addiction?
Identifying heroin addiction involves observing signs of drug use, evident in altered behavior, declining health, and neglect of responsibilities. Streets often witness the struggle as individuals succumb to the substance’s grip.
Addiction manifests in different ways, from physical symptoms like weight loss to mental distress. Heroin overdose looms as a grave risk, emphasizing the urgency of intervention.
Substance use disorders plague communities across the United States, demanding awareness and support. Learn these signs to foster a compassionate response to those battling heroin addiction. Collectively addressing this issue is pivotal for creating healthier and safer communities nationwide.
Rise Above With The Haven Detox-New England
At The Haven Detox-New England, we transcend addiction hurdles through different innovative ways.
Our dual diagnosis treatment addresses underlying issues, while our methadone-assisted treatment (MAT) program employs proven mechanisms for holistic recovery. Experience recovery through our diverse levels of care, ensuring personalized support at every step.
Call (844) 933-4145 for lasting recovery through personalized services.
Verify Insurance
Let’s get you or a loved one help with a few simple steps.




