People dealing with bipolar disorder experience intense emotional highs, called manic or hypomanic episodes, and lows, known as depressive episodes.
In this article, we will shed light on the various ways bipolar disorder can affect individuals. Understanding these signs is essential for timely diagnosis and successful management of this mental health condition.
Key Takeaways
Bipolar disorder involves extreme mood swings, impacting daily life, relationships, and well-being. Here is what this article covers:
- Bipolar disorder manifests in the form of manic, hypomanic, and depressive episodes, each with its own symptoms.
- Mixed episodes bring simultaneous highs and lows, requiring prompt recognition and comprehensive intervention.
- Effective management of bipolar disorder involves the combination of different treatment methods, such as medication and therapy.
Contact The Haven Detox-New England at (844) 933-4145 for comprehensive mental health care in overcoming different types of bipolar disorder.
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder marked by extreme mood swings, ranging from elevated energy and activity (mania or hypomania) to episodes of severe depression. There are two main types of bipolar disorder: Bipolar I and Bipolar II.
Bipolar I is marked by severe manic episodes that may last for at least seven days, often requiring hospitalization. These manic episodes can be accompanied by depressive episodes lasting around two weeks. Individuals with bipolar I may experience disruptions in their daily lives due to the intensity of these mood swings.
On the other hand, bipolar disorder II involves milder manic episodes, known as hypomania, and more prolonged periods of depression. While hypomania is less severe than full-blown mania, it can still lead to impaired functioning. People with bipolar II might initially seek help during depressive episodes, as the hypomanic episodes may be less noticeable.
The exact cause of bipolar disorder is not well understood, but a combination of genetic, biological, environmental, and social factors may contribute. It often first manifests in late teens or early adulthood, but it can occur at any age.
Bipolar disorder affects various aspects of everyday life, including relationships, work, and overall well-being. Accurate diagnosis and treatment are vital for managing signs and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with bipolar disorder.
Identifying Bipolar Disorder: Key Signs and Symptoms
Bipolar disorder, a mental health problem, is characterized by extreme mood swings or manic-depressive episodes. The signs and symptoms of different types of bipolar disorder can vary between individuals, and the severity of episodes can also differ.
Here are some common signs and symptoms of bipolar disorder:
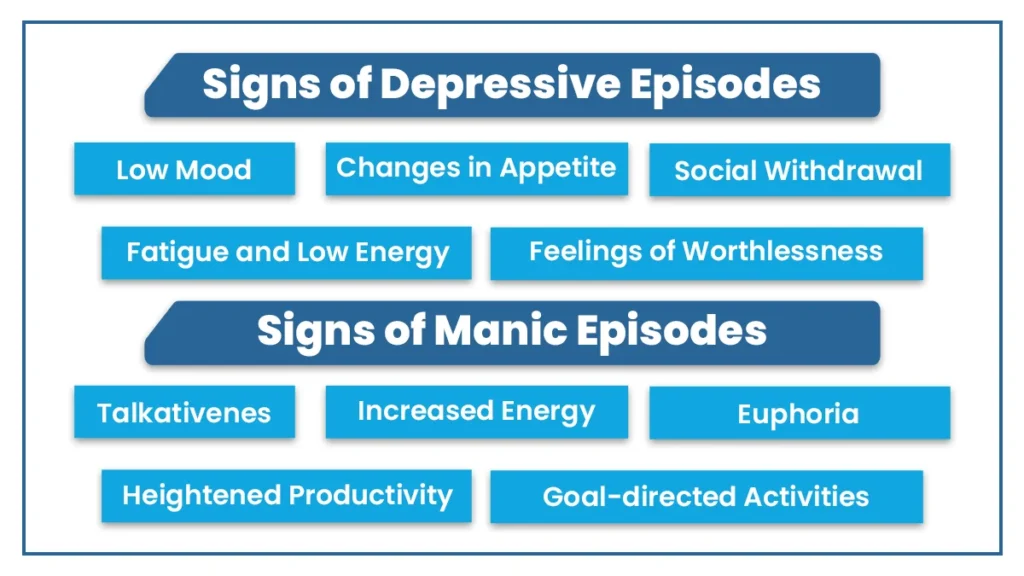
Signs of Manic Episodes
During a manic phase of bipolar disorder, individuals often experience an intense surge of energy and heightened mood. Here are the common manic symptoms:
- Elevated Energy Levels: Experiencing a sudden increase in energy and restlessness.
- Rapid Speech and Thoughts: Talking fast and having racing thoughts make communication challenging.
- Impulsive Behavior: Engaging in high-risk activities without considering consequences, like overspending or reckless driving.
- Decreased Need for Sleep: Feeling wide awake with minimal sleep, yet not feeling tired.
- Grandiosity: Exhibiting an inflated sense of self-importance and confidence.
- Distractibility: Struggling to focus on one task due to heightened distractibility.
- Psychotic Symptoms: In severe cases, experiencing delusions or hallucinations.
Signs of Hypomanic Episodes
Hypomanic episodes are the less severe form of mania. Individuals with hypomania may still function relatively well in their daily lives. Common signs include:
- Increased Energy and Euphoria: Feeling more energized than usual without the extreme highs of mania.
- Heightened Productivity: Becoming unusually productive and creative in various activities.
- Sociability and Talkativeness: A sudden increase in social interactions and talkativeness.
- Goal-directed Activities: Engaging in purposeful tasks with heightened focus.
- Lack of Social Impairment: Unlike episodes of mania, social and occupational functioning remains relatively intact.
- Potential for Escalation: Hypomanic states may escalate into full-blown mania in some cases.
Signs of Depressive Episodes
Episodes of depression are marked by consistent feelings of sadness and low energy. Common symptoms of depression are:
- Low Mood: Feeling down or hopeless for an extended period.
- Anhedonia: Losing interest in activities once found enjoyable.
- Changes in Appetite and Weight: Major changes in appetite, leading to weight loss or gain.
- Disrupted Sleep Patterns: Dealing with insomnia or hypersomnia regularly.
- Fatigue and Low Energy: Feeling constantly tired and lacking the usual energy levels.
- Cognitive Impairments: Struggling with concentration, decision-making, and negative thought patterns.
- Social Withdrawal: Avoiding social activities and isolating oneself.
- Feelings of Worthlessness and Guilt: Battling with self-esteem issues and persistent guilt.
- Suicidal Thoughts: In extreme cases, considering self-harm or suicide.
If you or a loved one are exhibiting bipolar disorder symptoms, seeking help from healthcare professionals is important for correct diagnosis and proper treatment.
Mixed Episodes in Bipolar Disorder
Mixed episodes in bipolar disorder are characterized by the simultaneous presence of symptoms associated with both manic or hypomanic episodes and depressive episodes.
This combination of symptoms can make the individual’s emotional state highly volatile and challenging to manage. It’s important to note that not everyone struggling with bipolar disorder will experience mixed episodes, and the intensity and duration of these episodes can vary.
Here are some common signs and symptoms of mixed episodes:
- Agitation: Individuals in a mixed episode may experience restlessness, nervousness, and overall agitation.
- Irritability: Intense irritability is common during mixed episodes. The person may be easily annoyed or angered, and their mood may quickly shift between elevated and depressed states.
- Racing Thoughts: A rapid flow of thoughts, similar to what is seen in manic episodes, may occur. This can contribute to increased anxiety and difficulty concentrating.
- Decreased Need for Sleep: Despite feeling depressed, individuals in a mixed episode may experience a reduced need for sleep. This can lead to insomnia and exacerbate other symptoms.
- Psychomotor Agitation: Physical restlessness and an increased pace of purposeless activities, such as pacing or hand-wringing, may be observed.
- Impulsivity: Mixed episodes can lead to impulsive behavior, similar to manic episodes. This may include reckless spending, substance abuse, or engaging in risky activities.
- Feelings of Despair: Despite the presence of manic or hypomanic symptoms, individuals in a mixed episode may still experience a profound sense of hopelessness and despair commonly associated with episodes of depression.
- Suicidal Thoughts: The combination of intense mood swings and depressive symptoms in mixed episodes can lead to a higher risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
If someone is showing signs of a mixed episode or if you are concerned about your mental health, seeking help from a mental health professional is indispensable for accurate diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
Managing Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder can be effectively managed through a combination of approaches, each playing a crucial role in promoting stability and well-being. Here are some treatment options for this medical condition:
Medication
Medication is a cornerstone in the management of bipolar disorder. Mood stabilizers, antidepressant medications, and antipsychotic medications are commonly prescribed to help regulate mood changes. Adhering to a prescribed medication regimen is essential for maintaining stability and preventing the recurrence of manic or depressive episodes. Regular, open communication with healthcare providers is key to adjusting medications based on individual responses and needs.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a valuable tool in managing manic-depressive disorder. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal and social rhythm therapy (ISRT) are approaches that can assist individuals in understanding and managing their emotions. Psychotherapy provides a safe space for exploring coping strategies, identifying triggers, and developing skills to navigate the challenges associated with bipolar disorder.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), a medical treatment, involves passing a carefully controlled electric current through the brain, inducing a brief seizure. While ECT is considered an effective treatment for certain mental disorders, including bipolar disorder and major depression, it is typically used when other treatments have not been successful or in emergencies.
Support Groups
Participating in mental health support groups provides individuals with bipolar disorder an opportunity to connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences, coping strategies, and mutual encouragement can foster a sense of community and lessen feelings of isolation. These groups, whether in-person or online, offer valuable insights and emotional support.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to professional interventions, lifestyle changes play a crucial part in managing the signs of a mental health problem. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a healthy diet contribute to overall well-being. Substance abuse avoidance and stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, further support a balanced lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do I know if I’m bipolar?
If you’re wondering if you have bipolar disorder, pay attention to extreme mood swings, ranging from intense highs to extreme lows. Notice if you experience impulsive behavior, changes in sleep patterns, and shifts in energy levels. If these signs persist, it’s crucial to consult mental health professionals for a complete evaluation and guidance.
What makes bipolar disorder worse?
Several factors can worsen bipolar disorder, including inconsistent medication adherence, substance abuse, high stress levels, and disruptions in sleep patterns. Identifying and addressing these triggers, along with maintaining a stable treatment plan, can significantly contribute to better management of bipolar symptoms.
How does a person with bipolar 2 think?
In bipolar II, individuals experience hypomanic and depressive episodes. During hypomania, thoughts may race, creativity can spike, and energy increases. In the low phases of bipolar disorder, thoughts may turn negative, leading to feelings of worthlessness and despair.
What are the signs of bipolar disorder in adults?
Signs of bipolar disorder in adults include extreme mood swings, ranging from manic or hypomanic episodes with elevated energy to depressive episodes marked by intense sadness. Changes in sleep patterns, impulsivity, irritability, and difficulty concentrating are common.
The Haven Detox-New England: Guiding You to Wellness
Discover a brighter tomorrow at The Haven Detox-New England, where hope and healing meet for those battling bipolar disorder.
Our inpatient rehab setting offers a lifeline to reclaim the happiness in your life. With expert medication management, evidence-based therapies, and holistic approaches, our comprehensive programs provide the support you need to overcome mental illness.
For those dealing with both mental health and substance use disorder (SUD), our dual diagnosis program is tailored just for you. We understand the unique struggles you face, and our team of experts is committed to guiding you toward lasting recovery.
Take the first step toward a life of balance and joy. Your journey to recovery begins now. Contact us today at (844) 933-4145 for more information.




